UZAY
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Digital Forensics
(Payload Interface Unit)
Digital forensics, particularly in the realm of image processing, involves the meticulous examination and analysis of digital images to uncover valuable evidence. This specialized branch of forensic science employs advanced techniques to detect, recover, and analyze visual data from various digital devices. By scrutinizing image metadata, identifying tampering or alterations, and enhancing image clarity, digital forensics experts can extract crucial information for legal investigations, cybersecurity, and law enforcement. The integration of image processing in digital forensics ensures accurate and efficient analysis, playing a pivotal role in solving crimes and verifying the authenticity of visual evidence.

Software Features
Features
At TÜBİTAK UZAY, various forensic softwares has been developed in areas such as Image/Video Geo-location, Image Camera Attribution, Social Media Detection, Brand Model Identification, Image Authentication, and Distance Estimation from Stereo Images. In all analyses performed, no prior information other than the visual content is required. For instance, in the Image/Video Localization Software, the coordinates from which a query image or video was taken are determined solely by examining its content. Additionally, with Image Camera Attribution Software, database queries can be conducted using the unique fingerprints extracted from the camera, regardless of the brand, model, or type of device. Using the Social Media Detection Software, it is possible to identify which social media channel a query image was downloaded from. The Brand Model Identification Software determines the brand and model family of a query image. The Image Authentication Software detects whether any malicious alterations, such as copy-move, splicing, or removing, have been applied to images. Finally, the Distance Estimation from Stereo Images Software calculates the absolute distances of points within a scene using two or more images.
Smart Security Systems
(Payload Interface Unit)

Software Features
Features
Security systems are made smarter with various artificial intelligence and pattern recognition methods, reducing the workload of security officers and ensuring more effective use. These methods include processes such as crowd analysis, traffic analysis, license plate recognition, face recognition, object tracking and concept recognition, starting from low-level background subtraction and becoming increasingly complex. Recognition of security-related concepts or event detection is complex as it targets an evaluation at the semantic level. Thus, it is still an important academic research topic.
With the software developed by TÜBİTAK UZAY, security-related semantic concepts are automatically recognized through visual and audio information and model-based learning is provided through labeled data. In the testing phase, the presence or absence of the searched semantic concept is determined by examining the suitability of the test data to the trained models. Learned models can be updated with new data, and the sensitivity of the system can also be adjusted. In this way, the risk of failure to detect due to false warnings can be minimized.
BALİSTİKA®
(Payload Interface Unit)
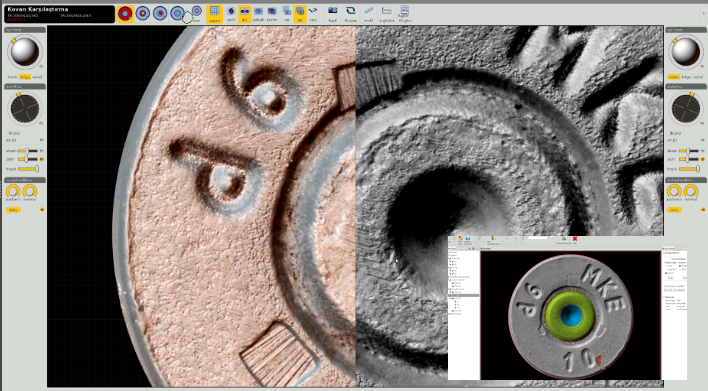
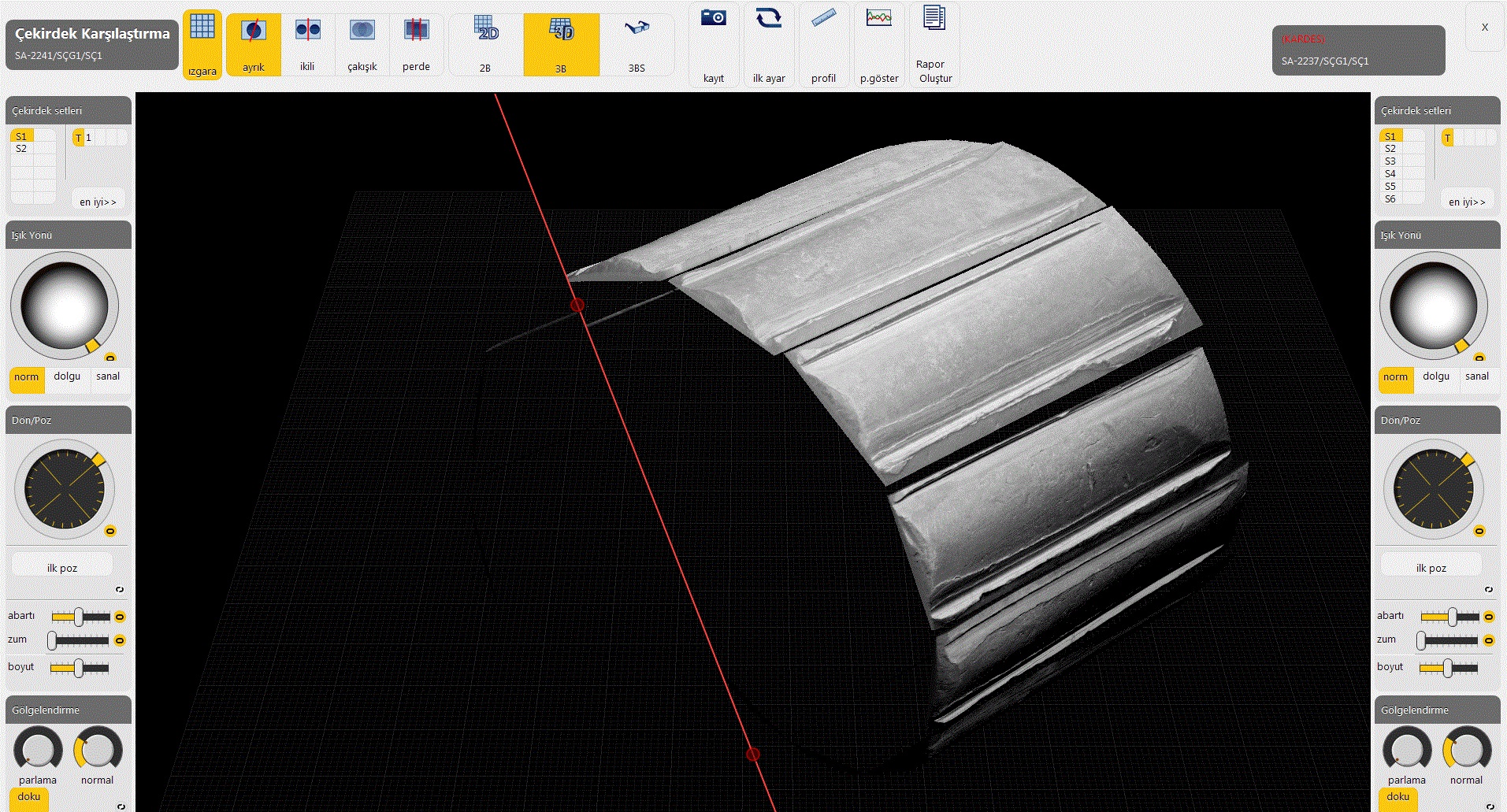
When firearms are used, they leave distinctive characteristic marks on the fired bullet and cartridge cases. By comparing these marks on two different bullets or cartridge cases, it can be determined whether they were fired from the same gun or not, and relationships between events can be established.
BALİSTİKA® is a system that obtains 3D data of bullet and cartridge cases, stores this data in a database with accompanying metadata, and can store information about events, individuals, and firearms. It generates features by extracting attribute data from 3D data, compare them, and provide the probability of being a match. The system is able to distribute the workload of the comparison process among the high computation power cluster, provide computer-based comparison of bullet and cartridge cases and exchange data with other BALİSTİKA® labs in different regions.

Cartridge Case Entry Unit
Features
The Cartridge Case Entry Unit is composed of high-tech hardware that allows for the capture of 3D cartridge case images. These images are obtained through the processing of 2D cartridge case images. The hardware is controlled through recording system software. It allows for the capture of images of cartridge cases with different diameters using a specially designed cartridge case holder. The capture of cartridge case images is easily completed without requiring additional settings from the user.
Hardware Features
- Creation of high-resolution 3D cartridge case images,
- Allowance for entry of cartridge cases with different diameters,
- Capturing the entire surface of the cartridge case in a single image,
- Specially designed cartridge case holder,
- Standardized capture of images without requiring user intervention in evidence image processing.
Bullet Entry Unit
Features
Bullet Entry Unit consists of hardware that enables the acquisition of 3D bullet images. This hardware is also controlled by recording system software like the Case Entry Unit. It allows the acquisition of 360 degree panoramic set images of the bullet. With the specially designed case holder, images of deformed bullets as well as bullet images of different diameter types can easily be obtained.
Hardware Features
- Creation of high-resolution 3D bullet images,
- Ability to acquire 360 degree panoramic set images,
- Ability to obtain images of deformed bullets,
- Simultaneous visualization of the entire surface of the bullet core,
- Standardized capture of images without requiring user intervention in evidence image processing.
Semantic Video Analysis
(Payload Interface Unit)

Software Features
Features
With the support of the Radio and Television Supreme Council (RTÜK), SKAAS (2006-20008) and KaVTaN (2008-2011) projects were carried out within TÜBİTAK UZAY in order to monitor, archive, and analyze terrestrial TV broadcasts. In this context, various softwares such as Video Shot Detection, Video-text Extraction, Video Program Analysis, Video Clip Retrieval, Keyword Detection and Radio Advertising Analysis have been developed, aiming to facilitate the analysis of experts watching broadcasting videos continuously.
Video Shot Analysis: Representing each scene with a key frame after automatically detects scenes within videos that allows a quick review of the video.
Video-Text Extraction: Detecting and recording the overlayed horizontal texts on videos that provides quick access to the video shots via text queries.
Video Program Analysis: Detecting broadcasts that do not comply with RTÜK regulations by determining the time and duration of terrestrial TV broadcast advertising slots.
Video Clip Retrieval: Determining on which channels, when and how many times a given query video clip was broadcast by searching in a previously created archive.
Keyword Detection: Finding the specified keywords in the audio data independent from speaker.
Radio Advertising Analysis: Identification of violations by automatically detecting radio advertising slots through audio data.
In addition, the ability to automatically perform semantic analysis visual and audio data has been developed, enabling automatic evaluation of large-scale terrestrial TV broadcast archive. For that purpose, a hierarchical ontology was created, five of which (violence, nudity, illegal organization, human detection, nature) are higher levels, and the concepts were trained with the labelled samples associated with each other in accordance with this ontology.

